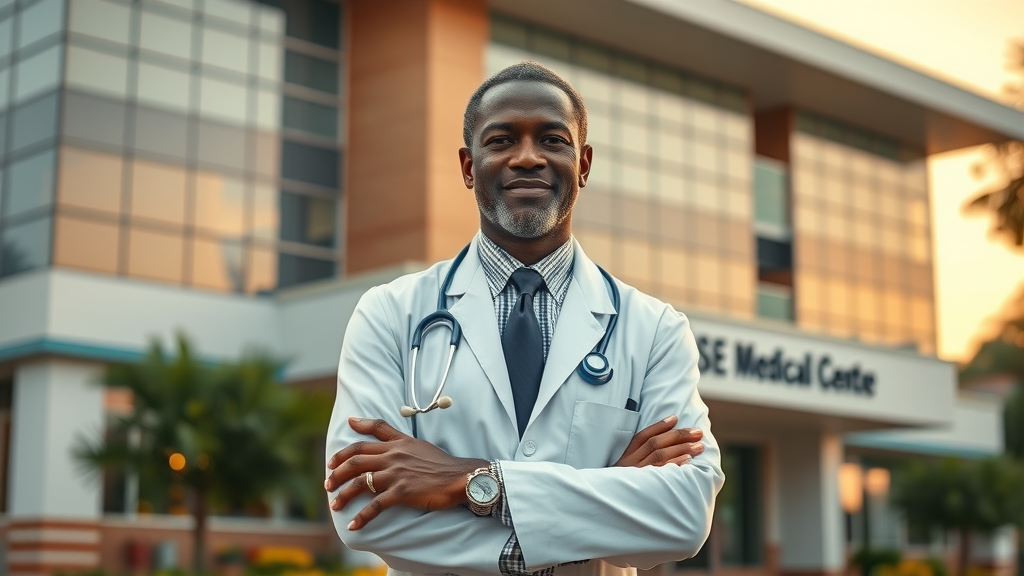
Did you know that in the 1990s, Uganda was one of the countries hit hardest by the HIV/AIDS epidemic, pushing its healthcare system to the brink? This stark reality laid the foundation for a remarkable journey of healthcare transformation in Uganda , driven by visionary leadership and innovative thinking. At the heart of this transformation is Dr. A.K. Sebbaale and the pioneering Case Medical Centre—a story of resilience, innovation, and hope.
Overview of Healthcare Transformation Uganda: Historical Context and Current Landscape

Uganda’s healthcare system in the 1990s faced unprecedented challenges due to the devastating HIV/AIDS epidemic. Hospitals and clinics were overwhelmed by patient loads, struggling under the weight of resource scarcity and limited medical infrastructure. Public hospitals were often under-resourced and overstretched, creating formidable barriers to quality care, especially in specialized fields.
During this critical period, healthcare workers were on the frontline of a crisis that demanded more than just medical know-how — it required innovation and steadfast commitment. It was within this historical context that Dr. A.K. Sebbaale began his medical career, fueled by his vision to redefine healthcare access and quality in Uganda.
-
The impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic on Uganda’s healthcare system in the 1990s
-
Challenges faced by public hospitals and clinics during early healthcare crises
-
Introduction to Dr. A.K. Sebbaale’s early career and vision
Founding Case Medical Centre: A Visionary Approach to Health System Reform
Dr. Sebbaale’s founding of Case Medical Centre marked a pivotal moment in healthcare transformation Uganda . Starting in 1995 as a modest outpatient clinic on Bombo Road, the centre gradually expanded to become a leading private tertiary hospital strategically located on Nakasero Hill. This growth reflected not only physical expansion but also the adoption of a philosophy grounded in healthcare as a fundamental right.
Case Medical Centre embodies this visionary approach, merging clinical excellence with patient-centered care. It has become a vital part of Uganda’s evolving health system, setting standards for quality, accessibility, and sustainability in private healthcare.
-
From a modest outpatient clinic to a leading private tertiary hospital on Nakasero Hill
-
Dr. Sebbaale’s philosophy on healthcare as a right, not a privilege
-
Role of Case Medical Centre in Uganda’s evolving health system
Dr. A.K. Sebbaale, of Case Medical Centre, explains, “Make quality healthcare a right, not a privilege.”
Health Insurance Innovation: Case MedCare’s Role in Financial Inclusion
Pioneering health insurance models have been a cornerstone of healthcare transformation Uganda , especially through Case MedCare—Uganda’s first Health Maintenance Organization introduced by Dr. Sebbaale under the Case group. This initiative addressed the critical barrier of healthcare affordability by offering accessible insurance solutions that empower individuals and businesses alike.
Case MedCare’s scalable and affordable HMO models serve as a dual engine combining clinical care excellence with financial protection. This innovative health insurance approach ensures that healthcare is not just a service but an inclusive right for a broader population.
-
Creation of Uganda’s first Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) under Case Group
-
Affordable, scalable health insurance models empowering individuals and corporations
-
The dual engine of clinical excellence and financial protection
“Insurance is not just about protection—it’s about inclusion,” says Dr. Sebbaale.

Community Health and Decentralization: Expanding Access Beyond Kampala
An essential dimension of healthcare transformation Uganda led by Dr. Sebbaale is the decentralization of health services through satellite clinics and community health initiatives. By establishing clinics beyond Kampala, Case Medical Centre has extended primary care and chronic disease management to underserved rural and peri-urban communities.
This approach not only reduces the strain on central hospitals but enhances community health outcomes through localized care delivery. The engagement of community health workers plays a crucial role in bridging gaps between formal health institutions and the populations they serve.
-
Development of satellite clinics offering primary care and chronic disease management
-
Role of community health workers in rural and peri-urban settings
-
Impact on reducing pressure on central hospitals and improving community health outcomes
Health Workers and Community Health: Bridging Gaps in Uganda’s Health System
Training and deploying community health workers have been vital in elevating healthcare access in Uganda. Through integration with the national health information systems, these workers facilitate health education, early diagnosis, and patient follow-up, significantly improving care continuity in remote areas.
This strategy enhances the flow of vital health information and strengthens data-driven decision-making across Uganda's health infrastructure—an indispensable element of healthcare transformation Uganda .
-
Training and deployment of community health workers
-
Integration with national health information systems
-
Enhancing health information flow and patient follow-up

Digital Health and Technology: The Next Scalpel in Healthcare Transformation Uganda
As Dr. Sebbaale emphasizes, the future of healthcare in Uganda hinges on the smart deployment of technology. Case Medical Centre is leading the introduction of telemedicine, AI-powered diagnostics, and robust mobile health platforms to bridge the gap between patients and providers.
By developing interoperable health information systems that connect public and private institutions, Uganda’s health sector is poised to reduce errors, speed up health worker training, and reach underserved regions more effectively. Digital health is not only a convenience but a critical catalyst in the ongoing transformation.
-
Integration of telemedicine, AI diagnostics, and mobile health platforms at Case Medical Centre
-
Development of interoperable health information systems connecting public and private providers
-
Reducing human error and accelerating health worker training through technology
Dr. Sebbaale emphasizes, “Technology will help us reach that last mile, reduce human error, and train faster.”

Health Information Systems and Digital Health: Enhancing Uganda’s National Health Infrastructure
Robust health information systems are foundational to the sustainability of healthcare transformation Uganda. The integration of digital tools facilitates coordinated care and enhances decision-making across varied health sectors, both public and private.
While challenges such as infrastructure constraints and data fragmentation exist, Case Medical Centre's leadership in digital innovations is setting a blueprint for health IT integration and national health system strengthening.
-
Role of digital health in strengthening Uganda’s health system
-
Challenges and opportunities in implementing health information systems
-
Case Medical Centre’s leadership in digital transformation
Leadership and Legacy: Dr. A.K. Sebbaale’s Enduring Impact on Uganda’s Health System
Dr. Sebbaale’s leadership throughout decades of healthcare challenges reflects remarkable resilience and vision. His unwavering commitment balances compassionate patient care with sustainable commercial practices—creating a replicable model of healthcare delivery that benefits Uganda’s population.
His work represents nation-building through innovation, inclusion, and reform, ensuring the health sector serves as a catalyst for social and economic development.
-
Resilience and reform through decades of healthcare challenges
-
Balancing compassionate care with commercial sustainability
-
Nation-building through healthcare innovation and inclusion
“Hope. Every patient that walks out of Case feeling better than they came in—that’s my reward,” reflects Dr. Sebbaale.

Common Challenges Facing Uganda’s Healthcare System
Despite significant strides, Uganda’s healthcare system still confronts several enduring challenges impacting the pace and scope of transformation. Limited public facility resources, financial barriers for many patients, workforce shortages, and gaps in technological adoption continue to restrict equitable access and quality of care.
Addressing these obstacles remains essential for sustaining momentum in healthcare progress across the nation.
-
Resource limitations in public health facilities
-
Financial barriers to accessing quality care
-
Workforce shortages and training gaps
-
Infrastructure and technology adoption hurdles
Health System Strengthening and Reforms in Uganda
Health system strengthening in Uganda is a multi-faceted effort involving government policy initiatives, dynamic public-private partnerships, and community-driven health education programs. Case Medical Centre exemplifies these efforts by bridging gaps in provision, financing, and education.
This collaborative movement aims to build a sustainable and inclusive health system that meets the diverse needs of its people while promoting innovation and accessibility.
-
Government initiatives and policy frameworks
-
Public-private partnerships exemplified by Case Medical Centre
-
Community engagement and health education programs
|
|
|
|
Healthcare Transformation Uganda: Challenges, Reforms, and Impacts |
|
Aspect |
Challenge |
Reform/Innovation |
Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Health Insurance |
Low coverage |
Case MedCare HMO |
Increased access and financial protection |
|
Health Workers |
Shortage and training |
Community health worker programs |
Improved outreach and care quality |
|
Health Information System |
Fragmented data |
Digital health integration |
Better coordination and decision-making |
|
Healthcare System |
Overburdened facilities |
Satellite clinics |
Decentralized care and reduced hospital load |

People Also Ask: Frequently Asked Questions on Healthcare Transformation Uganda
-
What is the status of the health care system in Uganda? Uganda’s healthcare system has made notable progress through reforms, but challenges such as resource gaps and access disparities persist. Both public and private sectors play key roles in ongoing transformation efforts.
-
What is the health system strengthening in Uganda? Health system strengthening involves policy initiatives, community engagement, and technology adoption aimed at improving service delivery, financing, workforce capacity, and health information management.
-
What are the health reforms in Uganda? Health reforms include decentralization of services, insurance innovation like HMOs, digital health integration, and public-private partnerships driving accessibility and quality improvements.
-
What are the challenges facing Uganda's healthcare system? Major challenges include limited resources, financial barriers, staffing shortages, and infrastructure deficits that hamper equitable healthcare delivery.
Key Takeaways: Insights from Dr. A.K. Sebbaale and Case Medical Centre
-
Healthcare transformation requires vision, resilience, and innovation.
-
Financial inclusion through health insurance is critical for improving access.
-
Community health workers and decentralized clinics expand reach and improve outcomes.
-
Digital health technologies are essential tools for future healthcare delivery.
-
Leadership grounded in compassion and sustainability drives lasting change.
Conclusion: The Future of Healthcare Transformation Uganda
-
Dr. Sebbaale’s ongoing mission continues to focus on expanding quality care and inclusion across Uganda.
-
The integration of technology and enhanced community engagement will shape the future health landscape.
-
Readers are encouraged to support and learn from Africa’s healthcare innovators for collective advancement.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment